- Aortic Stenosis
- Turbulent flow which begins at aortic valve
- Mild aortic regurgitation
- Aortic stenosis
- Turbulent flow which begins at the aortic valve by color Doppler
- No aortic regurgitation
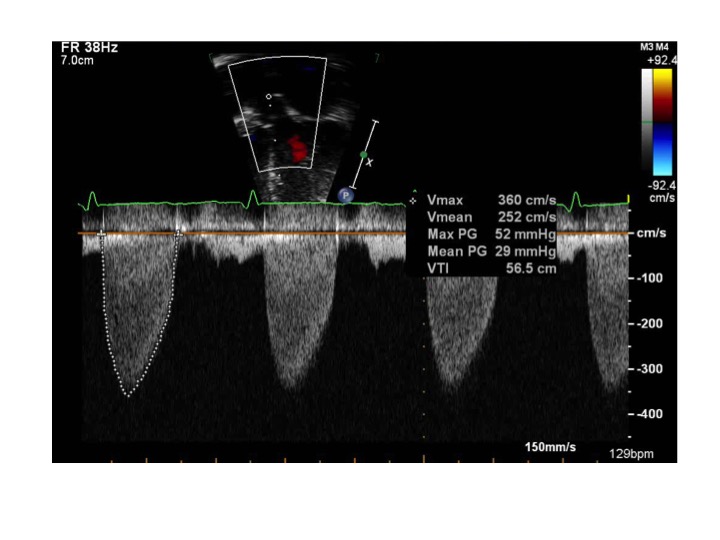
- Aortic stenosis
- Continuous wave Doppler across the aortic valve
- Spectral Doppler velocity consistent with mild to moderate aortic stenosis
Aortic Stenosis Severity
| Aortic Stenosis | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
| Peak velocity (meters/sec) | 2.6-3.0 | 3-4 | >4 |
| Mean Gradient | <20 (<30**) | 20-40*(30-50**) | >40*(>50**) |
| Aortic Valve Area (cm2) | >1.5 | 1.0-1.5 | <1.0 |
| Indexed Aortic Valve Area (cm2/m2) | >0.85 | 0.6-0.85 | <0.6 |
| Velocity Ratio | >0.5 | 0.25-0.50 | <0.25 |
*AHA/ACC guidelines
**ESC Guidelines
Source: Kyle, American Society of Echocardiography (ASE)
- Critical Aortic Stenosis
- Dysplastic thickened aortic valve with restricted excursion
- Thickened mitral valve leaflets with limited excursion with shortened chordae
- Severely depressed left ventricular systolic function
- Critical Aortic Stenosis
- Dysplastic thickened aortic valve with restricted excursion
- Flow turbulence across the aortic valve with narrow jet of flow across a severely stenotic aortic valve
- Thickened mitral valve leaflets with limited excursion with shortened chordae
- Severely depressed left ventricular systolic function
From the apical 5 chamber view, the severity of aortic valve stenosis is best assessed utilizing pulse and continuous-wave Doppler to measure the peak instantaneous and mean pressure gradients across the aortic valve (which can be assumed to be an accurate measure of stenosis only if the valve is the only site of left sided obstruction and the left ventricular function and cardiac output are preserved). This is also a good view to assess for aortic regurgiation.
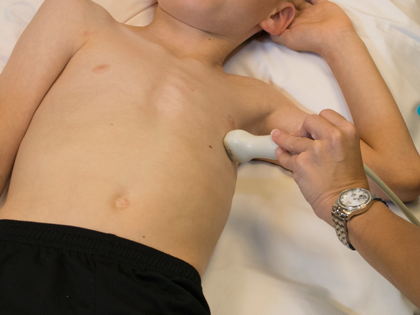
- Transducer at cardiac apex
- Notch at 3-4 o'clock (slight clockwise rotation)
- 4th or 5th intercostal space
- Probe tilted anteriorly (tail down)
- Aortic stenosis (quantification by spectral Doppler)
- Aortic regurgitation