- Transposition of the great arteries
- Aorta is anterior and rightward to the pulmonary artery
- The three aortic cusps are shown
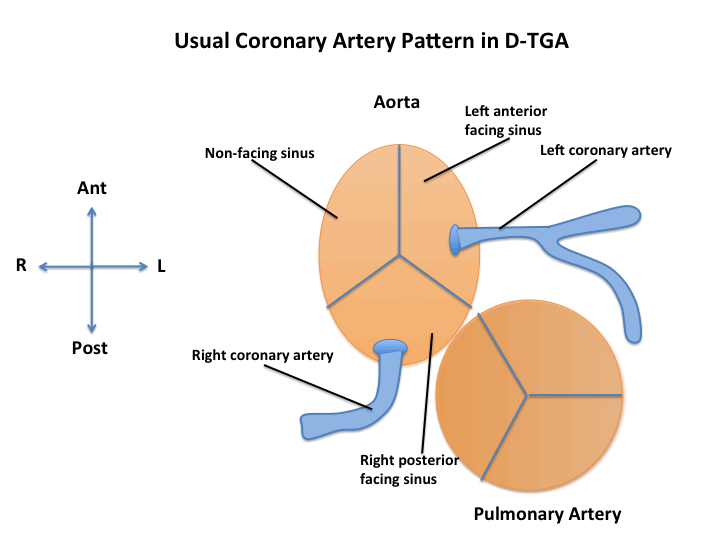
- Usual origin of left coronary artery arising from the anterior left facing sinus of Valsalva
- Transposition of the great arteries
- Aorta is anterior and rightward to the pulmonary artery
- The three aortic cusps are shown
- Usual origin of left coronary artery arising from the anterior left facing sinus of Valsalva with color Doppler flow demonstrated in the left coronary artery
- Transposition of the great arteries
- The three aortic cusps are shown
- The great arteries demonstrate an anterior/posterior orientation
- Usual origin of left coronary artery arising from the posterior left facing sinus of Valsalva with color Doppler flow demonstrated in the left coronary artery
- Transposition of the great arteries
- Aorta is anterior and rightward to the pulmonary artery
- The three aortic cusps are shown
- Usual origin of right coronary artery arising from the posterior right facing sinus of Valsalva
- Transposition of the great arteries
- The three aortic cusps are shown
- Usual origin of right coronary artery arising from the posterior right facing sinus of Valsalva with color Doppler flow demonstrated in the right coronary artery
- Transposition of the great arteries (D-TGA)
- Aorta is anterior and rightward to the pulmonary artery
- The posterior vessel pulmonary artery is seen bifurcating into the branch pulmonary arteries
- Transposition of the great arteries (D-TGA)
- Aorta is anterior and rightward to the pulmonary artery
- The posterior vessel pulmonary artery is seen bifurcating into the branch pulmonary arteries
- Moderate sized PDA is seen draining into the main pulmonary artery (red color Doppler flow)
- Transposition of the Great Arteries
- Parasternal short axis sweep
- The aorta is positioned anterior and rightward to the pulmonary artery
- The pulmonary artery is seen as the posterior bifurcating vessel
- Transposition of the Great Arteries
- Aortic and pulmonary valves shown en face
- Both valve appear tricommissural
- The aorta is positioned anterior and rightward to the pulmonary artery
The parasternal short axis view is a good view to profile the orientation and spatial position of the great vessels. In transposition, the aorta typically arises anterior and rightward to the pulmonary artery. The coronary arteries can also be profiled from this view.
The coronary arteries can also be profiled from this view. Typically the aorta is anterior and rightward to the pulmonary artery with the coronary artery ostia positioned in the following orientation:
- Left sternal border
- 3rd or 4th intercostal space
- Notch pointing towards left shoulder (1-2 o'clock)
- D-TGA (origin and position of great vessels)
- Coronary artery origin and course