- Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Large PDA seen entering the main pulmonary artery near the left pulmonary artery
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Large PDA seen entering the main pulmonary artery near the left pulmonary artery
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Large PDA with bidirectional shunting (left to right = red flow, right to left = blue flow)
- Patent Ductus Arterious
- Large PDA with continuous left to right shunting (red flow)
- Patent Ductus Arterious
- PDA with continuous left to right shunting (red flow)
- PDA appears to be large in size as it is as large as the left pulmonary artery
- Patent Ductus Arterious
- Small PDA with continuous left to right shunting (red flow)
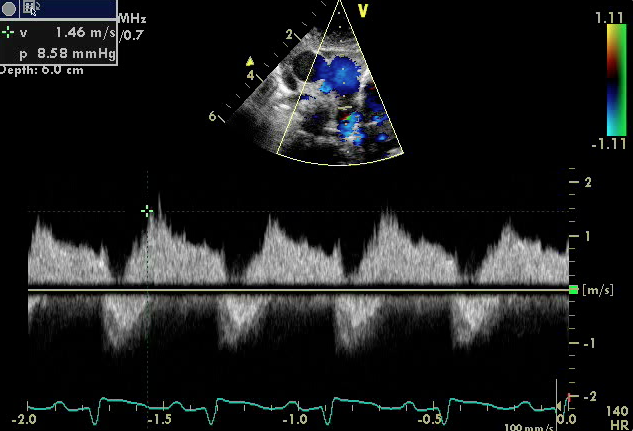
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Spectral Doppler demonstrating continuous left to right high velocity shunting (Doppler pattern above the baseline) in a small PDA
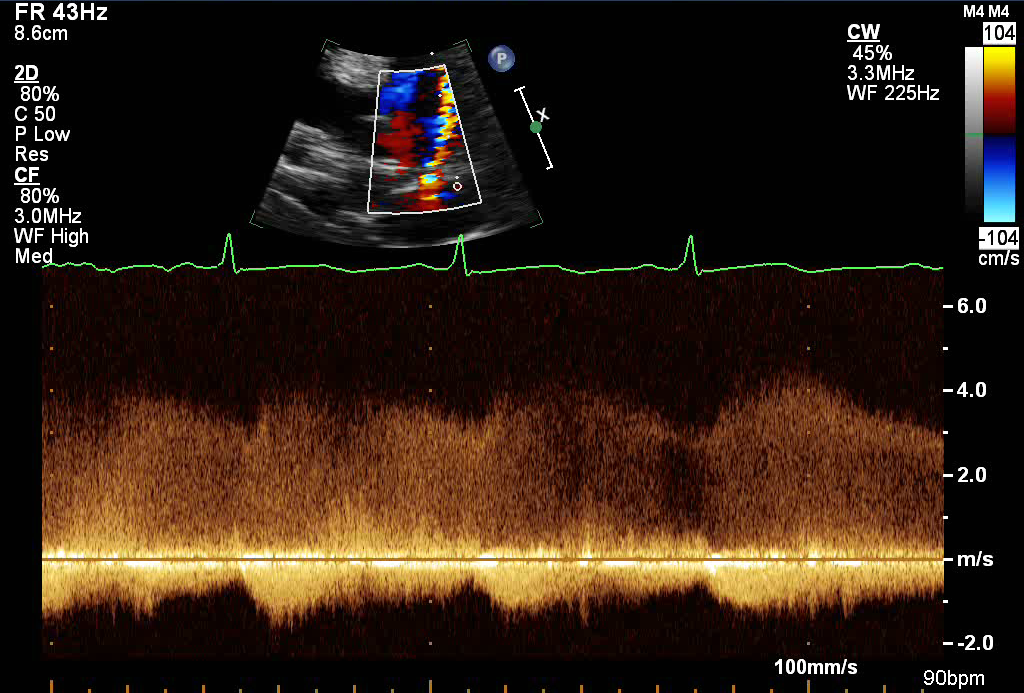
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Spectral Doppler of a large PDA with low velocity bidirectional shunting
- Left to right flow in diastole (above baseline)
- Right to left flow in systole (below baseline)
- Spectral Doppler of a large PDA with low velocity bidirectional shunting
Echocardiographic Assessment: Parasternal Short Axis
- PDA diameter (2D and color Doppler)
- measurement of the 2D diameter of the PDA at its narrowest point, usually at the pulmonary end
- Direction of PDA shunting by color and spectral Doppler (left to right, right to left, bidirectional)
- PDA peak velocity
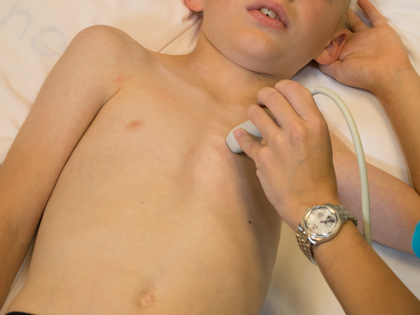
- Left sternal border
- 3rd or 4th intercostal space
- Notch pointing towards the left shoulder (1-2 o'clock)
- Transducer tilted superiorly and medially
- The ductal view is obtained by moving just out of the suprasternal notch (SSN) to the first left intercostal space.