- Pericardial Tamponade
- Large pericardial effusion
- Heart appears to swing as it is surrounded circumferentially by a large amount of fluid
- Pericardial tamponade physiology
- Right ventricular diastolic collapse
- Right atrial systolic collapse
- Pericardial tamponade physiology
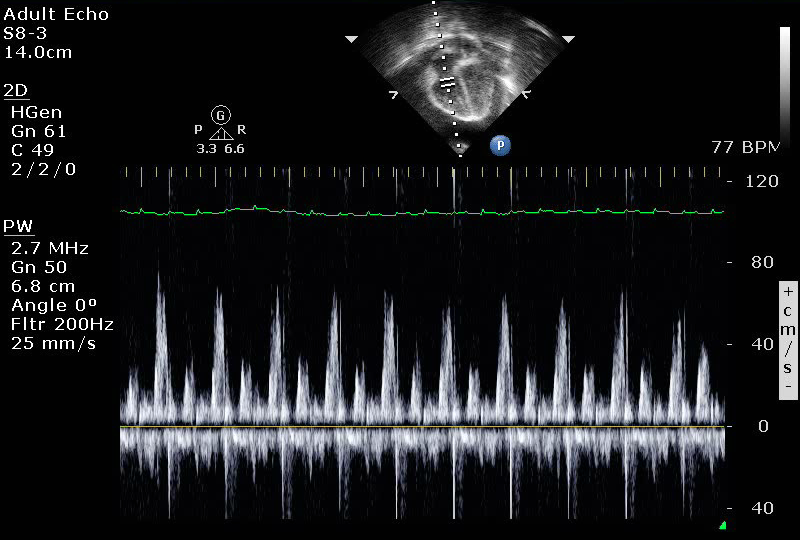
- Spectral Doppler across the tricuspid valve demonstrating marked inflow variation in patient with pericardial tamponade
- Pericardial tamponade physiology
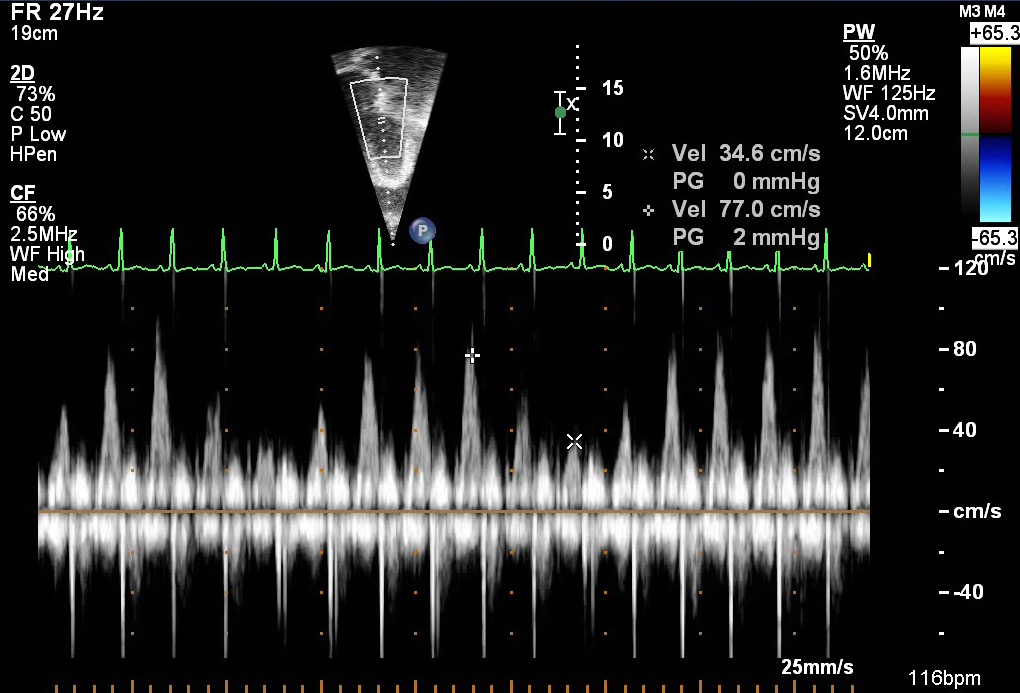
- Spectral Doppler pattern demonstrating inflow variation across the mitral valve in a patient with pericardial tamponade
- Pulse wave Doppler shows large variability in E-wave peak during inspiration versus expiration
- Inflow variability here is (77.0 cm/s – 34.6 cm/s) / 77.0 cm/s = ~55% (normal mitral inflow < 25%)
- Echocardiographic Assessment: Apical 4 Chamber
- Assess for pericardial effusion
- anteriorly, posteriorly, apically and circumferentially
- measure fluid by 2D at end diastole
- Assess for right ventricular diastolic collapse
- Asses for right atrial systolic collapse
- Assess ventricular systolic function qualitatively and by Simpson's biplane method
- Assess tricuspid and mitral valve inflow variability by spectral Doppler
- Pulse wave Doppler across the atrioventricular valves will show increased inflow variability (echocardiographic equivalent of pulsus paradoxus). Patient must be spontaneously breathing (not mechanically ventilated).
- Assess for pericardial effusion
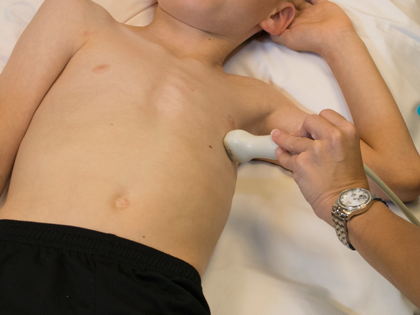
- Transducer placed on apical PMI (4th or 5th intercostal space)
- Midclavicular line at the apical PMI (point of maximal intensity)
- Notch at 3 o'clock