- Left Ventricular Noncompaction
- Moderately dilated globular appearing left ventricle
- Heavily trabeculated left ventricle, most pronounced in the apical and left ventricular free wall.
- Dyskinetic interventricular septum.
- Moderate to severely depressed left ventricular systolic function.
- Left Ventricular Noncompaction
- Moderately dilated globular appearing left ventricle
- Heavily trabeculated left ventricle with prominent trabeculations along the septum, apex and left ventricular free wall
- Moderate left atrial dilation
- Mild to moderately depressed left ventricular systolic function
- Left Ventricular Noncompaction
- MIldly dilated and heavily trabeculated left ventricle, most pronounced at the apex and free wall
- Dyskinetic interventricular septum
- MIldly depressed left ventricular systolic function with hypokinesis of the left ventricular apex and inferior septum and inferior lateral wall
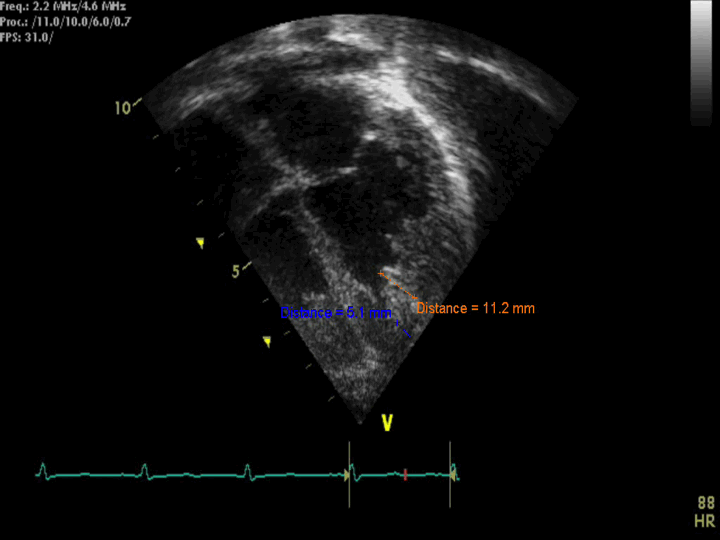
- Left Ventricular Noncompaction
- Still frame of measurment of non compacted to compacted ratio ~2.2 at end systole (abnormal >2)
- Echocardiographic Assessment: Apical 4 chamber
- Assess for left ventricular trabeculations, and segment of left ventricle where the trabeculations are more pronounced.
- Assess left ventricular systolic and diastolic function.
- Measure the Noncompacted/compacted ratio in end-systole.
- Pulse wave (PW) tissue Doppler (TDI) of left ventricular free wall at the level of the mitral valve are used for evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function, and also to help calculate the E/E’ ratio (using the peak mitral E wave velocity divided by the E’ from the PW TDI of the lateral mitral valve annulus, normal E/E' ratio <10).
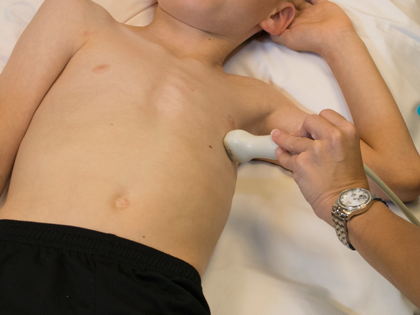
- Transducer placed on apical PMI (4th or 5th intercostal space)
- Midclavicular line at the apical PMI (point of maximal intensity)
- Notch at 3 o'clock