- Supracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Pulmonary veins seen draining into a confluence
- Supracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Color Doppler demonstrating pulmonary veins draining an anomalous to a confluence
- The pulmonary veins demonstrate normal laminar flow and do not appear to be obstruction as they drain into the confluence
- Supracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Vertical vein ascends superiorly and drains into the innominate vein
- Supracardiac total anomalous pulmonary venous return
- Vertical vein ascends and drains into the innomminate vein
- Vertical vein passes anterior to the left pulmonary artery
- Typically no obstruction if vertical vein passes anterior to left mainstem bronchus and left pulmonary artery
- In some caes, vertical vein passes between left pulmonary artery and left mainstem bronchus causing pulmonary venous obstruction
- Supracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Vertical vein ascends and drains into the innominate vein
- Vertical vein flow becomes turbulent as it passes over the left pulmonary artery
- Vertical vein travels between the left pulmonary artery and mainstem bronchus with compression causing pulmonary venous obstruction
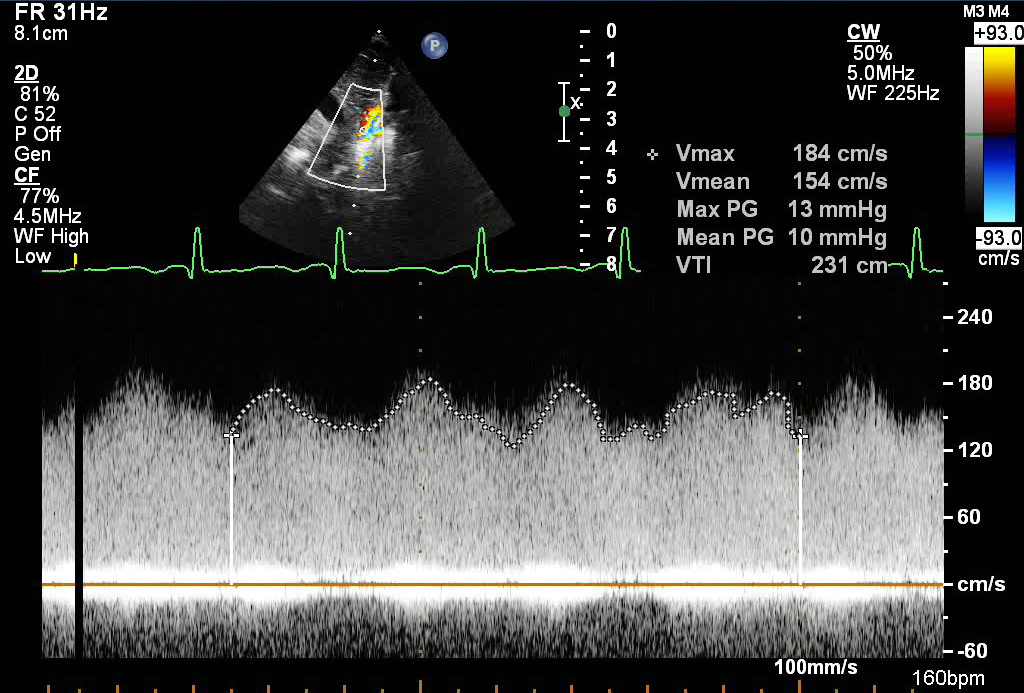
- Supracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Spectral Doppler in the vertical vein revealing obstruction along its course of the vertical vein
- Obstruction most common as vertical vein passes between left pulmonary artery and left bronchus
Supracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Color compare sweep demonstrating an ascending vertical vein
- There appears to be obstuction as the vertical vein passes between the left pulmonary artery and left bronchus ("physiologic vice") with flow turbulence starting in this region
- The vertical vein ultimately drains into the left innominate vein which continues into the SVC seen at the end of this sweep
Supracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Color compare sweep demonstrating an ascending vertical vein
- There appears to be obstuction as the vertical vein passes between the left pulmonary artery and left bronchus ("physiologic vice") with flow turbulence starting in this region
Supracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Color Dopper in an ascending vertical vein
- There appears to be obstuction as the vertical vein passes between the left pulmonary artery and left bronchus ("physiologic vice") with flow turbulence starting in this region
Supracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Color compare view demonstrating two left and one right pulmonary vein (veins represented by stars) draining into a confluence with an ascending vertical vein
- There appears to be obstuction as the vertical vein passes between the left pulmonary artery and left bronchus ("physiologic vice") with flow turbulence starting in this region
Echocardiographic Assessment: Suprasternal Notch
- Pulmonary venous confluence
- Assess individual pulmonary veins as they drain into confluence by 2D, color and spectral Doppler
- Vertical vein anatomy and course
- Assess by color Doppler for evidence of turbulence/obstruction (most commonly between left pulmonary artery and left mainstem bronchus)
- Assess by spectral Doppler for evidence of obstruction
- Innominate vein
- Size and flow by 2D, color and spectral Doppler
- Assess for connection to veritcal vein
- Superior vena cava
- Size and flow by 2D, color and spectral Doppler
- Assess for connection to vertical vein
- Probe at suprasternal notch
- Notch at 3 o'clock
- Transducer tilted posteriorly (tail up)
- May have to slide probe inferiorly along the left side of sternum with a posterior inferior tilt of the transducer (tail up) to fully profile pulmonary veins