- Coarctation of the aorta in the region of the aortic isthmus
- Posterior shelf noted in this region with severe anatomic narrowing
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Turbulent flow in the region of the aortic isthmus with persistence of flow into diastole
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Posterior shelf noted in aortic isthmus with severe anatomic narrowing
- Displacement of the left subclavian artery (elongated distance between left carotid and left subclavian artery)
- Turbulent flow in the region of the aortic isthmus with persistence of flow into diastole
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Narrowing of aortic isthmus
- Turbulent flow with persistence of flow into diastole
- Large PDA with bidirectional shunting
- Right to left (blue flow)
- Left to right (red flow)
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Critical coarctation with severe narrowing of the aortic isthmus
- Turbulent blood flow noted across narrow coarctation
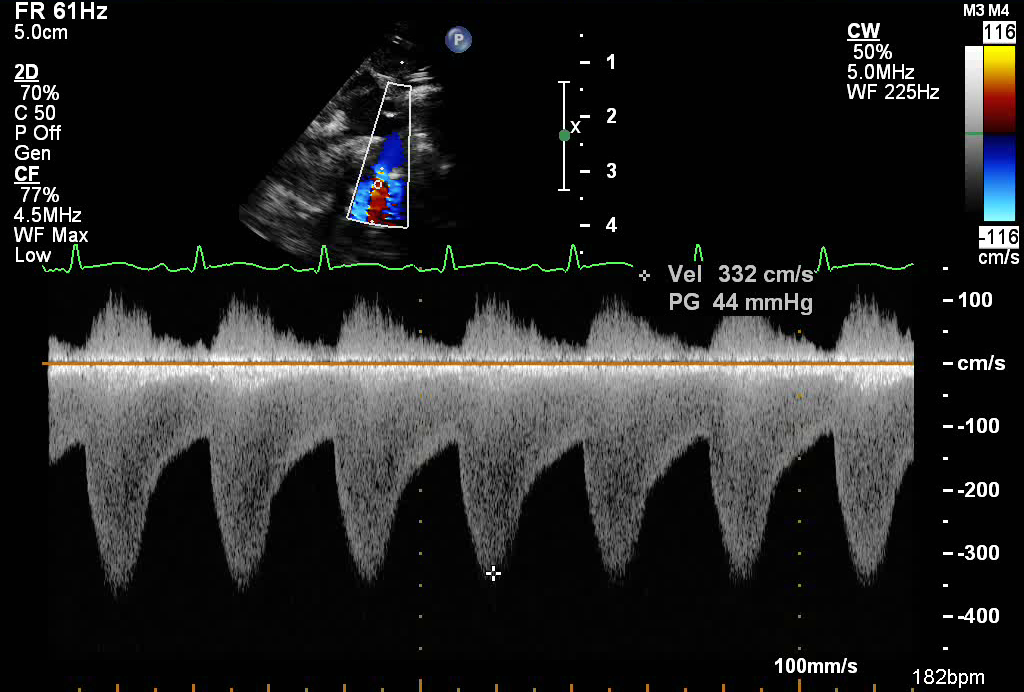
- Continuous wave spectral Doppler in the descending aorta in patient with coarctation (below baseline)
- High velocity flow (up to 3 meters/sec)
- Persistence of flow into diastole (also known as diastolic runoff)
The suprasternal notch view is an ideal view for profiling the aortic arch and assessing for arch hypoplasia and the presence of a coarctation.
.png)
- Probe placed in suprasternal notch
- Notch pointed towards 1 o'clock
- Tilt inferiorly and anteriorly
- Aortic arch hypoplasia
- Coarctation of the aorta