Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
- A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is an abnormal communication between the right ventricle and left ventricle
- A VSD can be a single defect or multiple defects.
- A VSD can be found in isolation or associated with numerous variants of congenital heart disease (i.e.- TOF, truncus arteriosis, PA/IVS, transposition of the great arteries)
Epidemiology
- Approximately 20% of all CHD
- Incidence varies widely (5-50/100,000) and is likely underestimated
- secondary to spontaneous closure of smaller defects in fetal life and early postnatal life
- Slightly greater prevalence in females
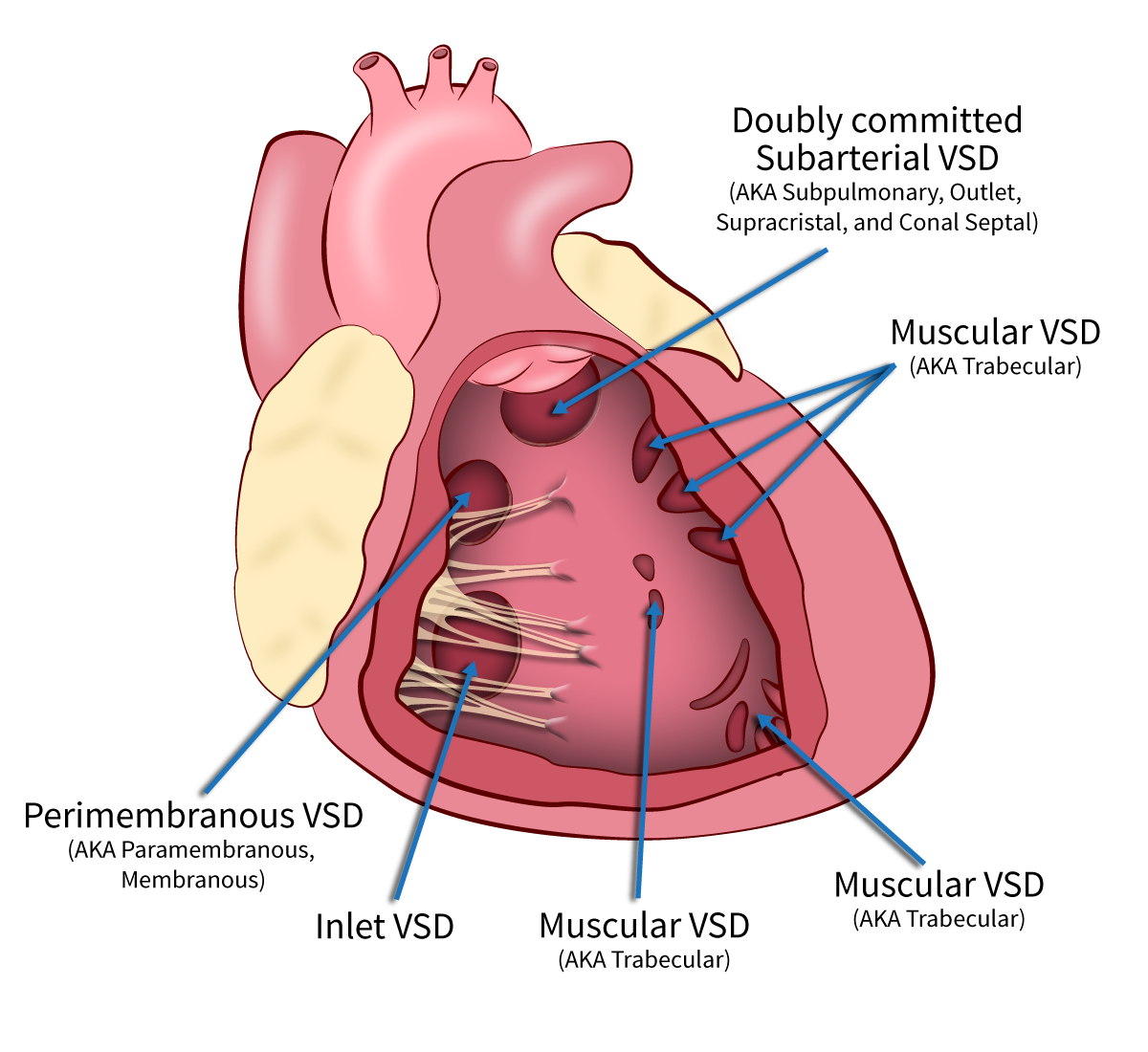
Types of VSDs
- Perimembranous (aka paramembranous, membranous) (80%)
- Muscular (aka trabecular) (5–20%)
- Doubly Committed Subarterial (aka conal septal, doubly committed juxta-arterial, subpulmonary, supracristal, outlet) (5–7%)
- Inlet (aka AV canal type) (5–8%)
Views