- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Severely dilated right atrium
- Severe right ventricular hypertrophy
- Moderate RV dysfunction
- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Mild to moderate tricuspid regurgitation from a severely pressure loaded right ventricle
- Severe right atrial dilation
- Severe right ventricular hypertrophy
- Pulmonary Stenosis
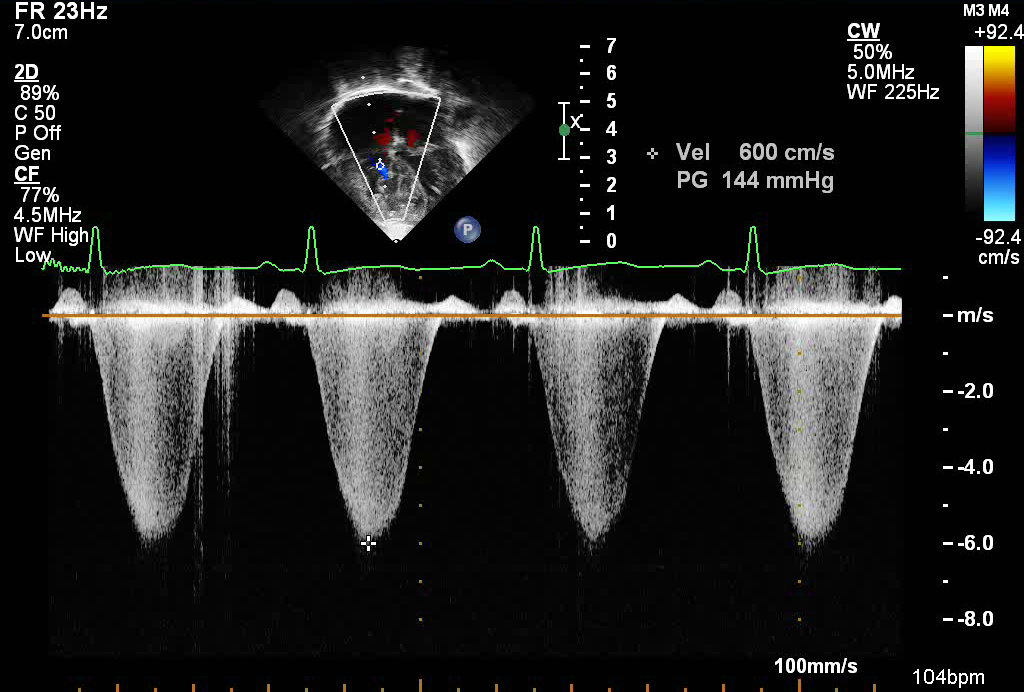
- Spectral Doppler from tricuspid regurgitation jet
- Suprasystemic right ventricular pressures in patient with severe pulmonary stenosis
- Estimated right ventricular systolic pressures of 144 mmHg + right atrial pressure
- Spectral Doppler from tricuspid regurgitation jet
- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Apical 4 chamber tilted anteriorly to profile RVOT and pulmonary valve
- Pulmonary valve stenosis noted with flow turbulance across the pulmonary valve
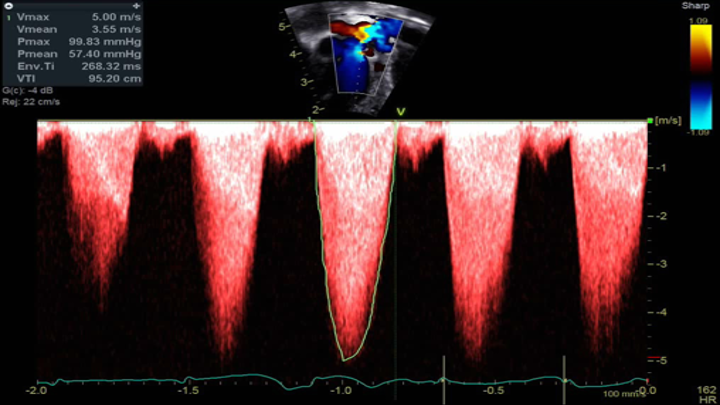
- Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
- Apical view angled anteriorly towards the pulmonary valve
- Continuous wave Doppler across the pulmonary valve revealing severe pulmonary valve stenosis
- Echocardiographic Assessment: Apical 4 Chamber
- Assess right atrial size
- Assess tricuspid valve size and morphology
- Assess for hypoplasia, dysplasia, restricted diastolic excursion
- Assess for tricuspid regurgitation
- Obtain a peak tricuspid regurgitation velocity to estimate RV systolic pressure (using Bernoulli equation)
- Assess RV/LV size and function
- Sweep anteriorly towards pulmonary outflow
- Assess any subvalvar obstruction due to presence of muscle bundles or right ventricular hypertrophy, and any component of dynamic right ventricular outflow obstruction.
- Evaluate pulmonary valve leaflet morphology.
- Assess for subvalvar or valvar pulmonary stenosis or regurgitation by color and spectral (pulse and continuous wave) Doppler
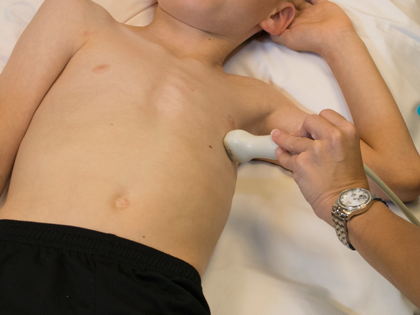
- Transducer placed on apical PMI (4th or 5th intercostal space)
- Midclavicular line at the apical PMI (point of maximal intensity)
- Notch at 3 o'clock