- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Critical pulmonary stenosis
- Severely hypertrophied right ventricle
- No appreciable flow across the pulmonary valve
- Retrograde flow from the PDA into the main pulmonary artery
- Severely depressed RV systolic function
- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Thickened dysplastic pulmonary valve with restricted excursion
- Post-stenotic dilation of the main pulmonary artery
- Normal biventricular systolic function
- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Thickened dysplastic pulmonary valve with restricted excursion
- Narrow jet of turbulent flow noted across the pulmonary valve
- Dynamic RVOT obstruction with flow turbulence of RVOT
- Post-stenotic dilation of the main pulmonary artery
- Mild pulmonary regurgitation
- Normal biventricular systolic function
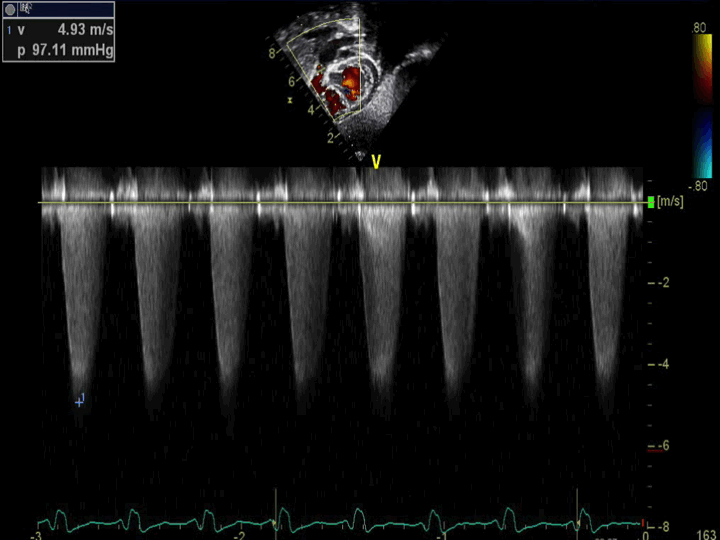
- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Continuous wave Doppler across the pulmonary valve demonstrating severe pulmonary valvar stenosis
- Echocardiographic Assessment: Subcostal Short Axis:
- Assess right ventricular outflow tract for stenosis (2D, color and spectral Doppler)
- Assess pulmonary valve morphology (2D)
- Assess for pulmonary valvar stenosis or regurgitation (color, spectral Doppler)
- This view is optimal to assess degree of stenosis as it has a very parallel angle of interrogation
.png)
- Transducer on abdomen just below xyphoid process
- Notch at 6 o'clock
- Tilt the ultrasound probe leftward