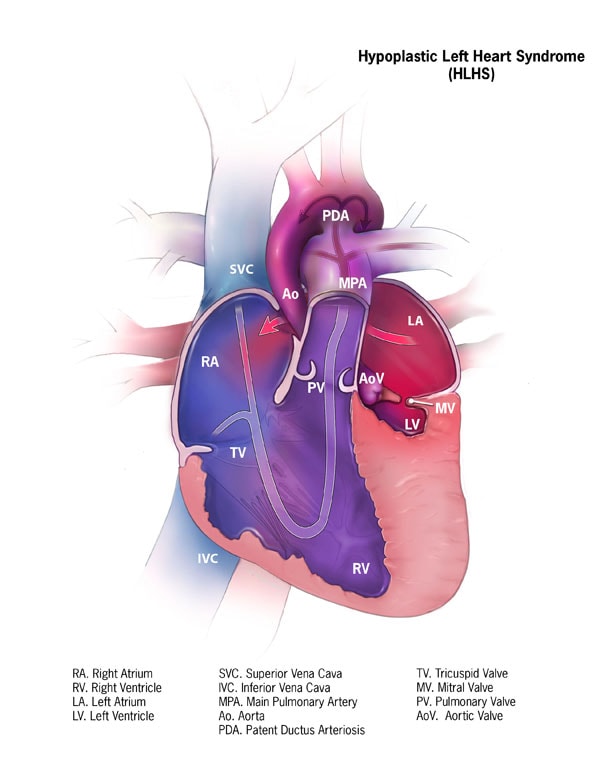
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS)
Hitesh Aggarwal, MD
Overview
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a variant of congenital heart disease which is characterized by an underdevelopment of the left sided cardiac structures (mitral valve, left ventricle, aortic valve and aortic arch). In HLHS, the left side of the heart is unable so support the systemic circulation. Blood returning from the lungs must flow through an atrial septal defect. The right ventricle pumps the blood into the pulmonary artery and blood reaches the systemic circulation through a patent ductus arteriosus. There is severe hypoplasia of the left ventricular cavity with a dominant right ventricle and systemic outflow tract obstruction.
Epidemiology/Genetics
HLHS comprises 1.4-3.8% of all congenital heart disease. There is growing evidence to suggest a genetic etiology but so far, no specific genetic abnormality has been linked to HLHS. With one affected family member, there is about 2.2-13.5 % risk of recurrence of other congenital heart disease in the same family.
Anatomy / Classification
HLHS occurs in a spectrum ranging from
- Aortic valve atresia with mitral atresia (AA/MA)
- Aortic valve atresia with a patent mitral valve with stenosis (AA/MS)
- Aortic stenosis with a patent mitral valve with stenosis (AS/MS).
Other common congenital abnormalities
- Coronary cameral fistulas are seen in patients with aortic atresia with a patent mitral valve.
- An intact or restrictive atrial septum occurs in 1% of neonates with HLHS.
- Persistent left superior vena cava occurs in 15% and anomalous pulmonary venous drainage in 5-10%.
Clinical presentation
HLHS is usually diagnosed via prenatal ultrasound given the advancement in fetal echocardiography. Such patients get started on PGE postnatally to maintain ductal patency until stage I palliation can be performed. Fetuses with critical aortic stenosis (who may evolve into HLHS variants) may be candidates for fetal aortic valvuloplasty. Likewise, those with restrictive/intact atrial septum are candidates for placement of intra-atrial stent during fetal life in the immediate postnatal period.
Children born without a prenatal diagnosis can have variable clinical manifestations. Those with restrictive/intact atrial septum develop cyanosis and respiratory distress early on while those with a non-restrictive atrial communication can appear acyanotic initially and come to medical attention with closure of PDA and exhibit signs of poor systemic perfusion such as respiratory distress, pale, cool extremities, lethargy etc.
Goals of echocardiography
In general echocardiography provides all the anatomic details needed for surgical planning of patients with HLHS.
Parasternal long axis:
- A small muscle bound, non-apex forming left ventricle is characteristic.
- The endocardial surface of the left ventricle can be echo-bright which is also known as endocardial fibroelastosis.
- The left atrium is generally small, but can be dilated in the setting of a restrictive atrial septum.
- The ascending aorta is hypoplastic with/without a patent aortic valve.
- The mitral valve is often imperforate, but if it is patent, the leaflets are thick, with short or even absent papillary muscle chordal attachments.
- Interrogation of the ventricular septum may show ventriculo-coronary arterial connections especially in cases of aortic atresia with patent mitral valve.
Parasternal short axis:
- This is a good view to assess left ventricular size and systolic function and mitral valve papillary muscles.
- The aortic valve morphology, left ventricle to coronary artery connections if present, pulmonary valve, the PDA continuing into the descending aorta and the branch pulmonary arteries can be visualized from this view.
Apical four chamber view:
- Additive information on the size and systolic function of the ventricles can be obtained.
- The mitral and tricuspid valve anatomy and annulus measurements can be obtained.
Subcostal view:
- This is the best view for atrial septal interrogation. Assess for the presence and size of an atrial communication. Both mean and peak Doppler gradients should be obtained which gives an estimate of left atrial hypertension. Estimating whether there is restrictive atrial level shunting is critically important postnatally as patients may require urgent balloon atrial septostomy in this setting.
- The pulmonary venous drainage can be assessed from this view. Even with normal pulmonary venous connection, if there is left atrial hypertension from restrictive/intact atrial septum, a levoatrial cardinal vein can be present which drains some or all pulmonary venous blood to a systemic vein.
Suprasternal notch view:
- The aortic arch anatomy including coarctation/arch interruption can be seen from this view. Doppler interrogation can visualize retrograde systolic flow in the aortic arch from a patent ductus arteriosus.
- Additional information on pulmonary venous drainage, left superior vena cava, levo-atrial cardinal vein, ductus arteriosus, and proximal branch pulmonary arteries can be obtained.