Pulmonary Atresia with Intact Ventricular Septum (PA/IVS)
Chris Wilkenson, MD
Overview and Natural History
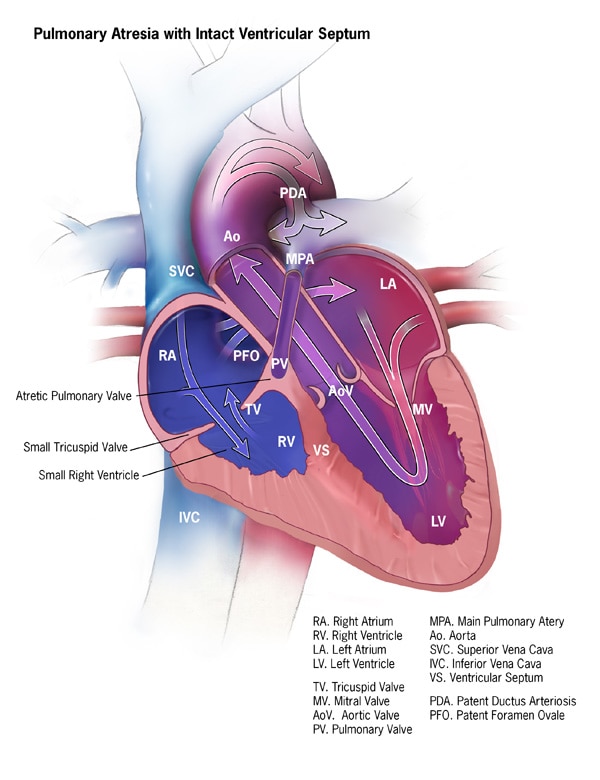
Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum (PA/IVS) is characterized by atresia of the pulmonary valve. The pulmonary valve is imperforate by way of a membranous or thicker muscular atresia. The ventricular septum is intact and pulmonary blood flow is dependent on a patent ductus arteriosus. PA/IVS is a disease with significant heterogeneity based on multiple anatomic factors including the degree and form of pulmonary atresia, the size of the right ventricle and tricuspid valve (both of which often demonstrate significant degrees of hypoplasia). In addition, the coronary circulation is often abnormal with an association between the RV and subepicardial coronary arteries or more typically called “RV dependent coronaries.” This lesion will typically present in the neonatal period and depending on multiple factors, can be managed with a biventricular repair, single ventricle palliation or, one and a half ventricle pathway or cardiac transplantation (usually reserved for the most severe variants with severe coronary disease and ventricular dysfunction).
Epidemiology
PA/IVS is found in about 6 to 8.3 in 100,000 live births. This number is thought to be an underestimation due to the frequency of fetal or in utero termination.
Genetics
There is no sex predilection or identifiable genetic cause known at this time.
Types
PA/IVS is a complex lesion with heterogeneity in procedural pathways, prognosis, as well as anatomic variance. The important characteristics in PA/IVS:
- Pulmonary atresia: imperforate due to membranous or thicker muscular atresia. Typically the morphology of the pulmonary valve will correlate with the character of the right ventricle. If the RV is well formed, the pulmonary valve is likely to have complete fusion of the cusps and commissures causing a membranous atresia. On the other hand, if the RV is diminutive, there is likely to be a primitive pulmonary valve and severely narrowed or atretic infundibulum or muscular atresia.
- Right ventricular features: There is a wide range of heterogeneity in the RV size, its inlet, tricuspid valve competency and function. The RV may range from a fully developed tripartite structure to a severely underdeveloped and hypoplastic inlet RV. Studies have shown the Z-score of the tricuspid valve to be associated with the size of the right ventricular cavity.
- Abnormal coronary circulation and development of ventriculocoronary connections: Typically due to subepicardial coronary arteries, development of sinusoidal or fistulous connections depending on the RV pressure. Typically, the RV-dependent coronaries develop due to absent aortocoronary connections, coronary artery interruption or stenosis or profound coronary-cameral steal or fistula.
Additional important features and characteristics:
- Tricuspid valve: typically abnormal with quite wide range of dysplasia, hypoplasia and competency. This is typically secondary to the issue that blood flow has no egress and must regurgitate. This as well as restriction of the tricuspid valve leaflets and chordae secondary to high right-sided pressures.
- In the majority of cases the branch pulmonary arteries are confluent and fed by a left-sided patent ductus arteriosus. Rarely, discontinuous pulmonary arteries are supplied by bilateral ducti or aortopulmonary collaterals.
Hemodynamics
The hemodynamics can differ greatly depending on the specific constellation of anatomic variance. There will be progressive cyanosis in the early neonatal period. They will typically be a murmur related to the degree of tricuspid valve regurgitation as well as a ductal murmur. These patients will need prostaglandin infusion in the neonatal period to ensure patency of the patent ductus arteriosus in order to maintain adequate pulmonary blood flow.
Goals of Echocardiography Exam
- Right ventricular morphology
- Associated right ventricular anomalies including malformations of the tricuspid valve such as Ebstein’s anomaly.
- Right ventricular inflow and outflow dimensions
- Coronary dilation or fistulous formations which can be very difficult to define by echocardiography (often require a CT scan or cardiac catheterization to define coronary arteries and to assess for RV dependent coronary circulation)
- Confirm pulmonary atresia, presence of pulmonary arterial leaflets
- Confirm the ventricular septum is intact
- Confirm coronary anatomy, presence of fistulous connections from RV
- Branch pulmonary artery size and whether the branch pulmonary arteries are in continuity
- Presence of pulmonary blood flow from an arterial ductus
It is recommended to use high-frequency probes and small sector width to optimize high spatial and temporal resolution. Generally, 3-5 beat clips are preferred and still frames should be avoided.