Truncus Arteriosus
Allison Doucet, RDCS (AE, PE)
Truncus arteriosus (TA) is a rare form of congenital heart disease occurring in 1-3% of patients with congenital heart disease. During fetal development, the embryonic truncus arteriosus gives rise to the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Persistent truncus arteriosus results from incomplete or failed septation. It is characterized by a single great artery arising from the heart with a single semilunar valve that overrides the right and left ventricles. The common trunk gives rise to the pulmonary arteries, providing systemic, pulmonary and coronary perfusion. A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is most commonly associated with TA, as well as anomalies with truncal valve, aortic arch and coronary arteries (outlined below). TA has a high association with 22q11 Deletion Syndrome (DiGeorge Syndrome) in ~20% of cases. There are four sub types of truncus arteriosus which are described using two different classification systems (outlined below). Type I/A1 is the most common form, found in ~60% of patients with Truncus Arteriosus.
Surgical repair is required due to likely development of congestive heart failure. If left untreated, the majority (up to 88%) of patients die in infancy due to heart failure from truncal valve regurgitation or pulmonary overcirculation. Surgical repair consists of a Rastelli operation where the VSD is closed via a baffle patch, the branch pulmonary arteries are removed from the common trunk and connected to a right ventricle to pulmonary artery conduit and if needed (in the setting of truncal stenosis and/or regurgitation), repair of the truncal valve is performed.
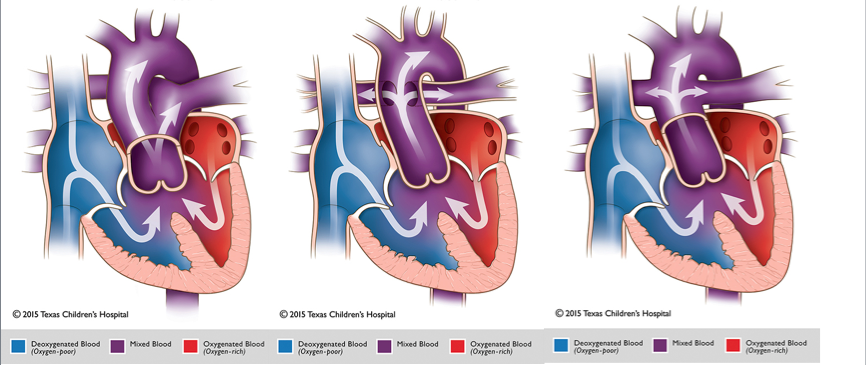
Classification Systems:
The Collett and Edwards system is the earliest form of classification, developed in 1949. It is based on where pulmonary arteries arise from the common trunk.
- Type I: The main pulmonary is present and bifurcates into the left and right pulmonary arteries
- Type II: the right and left branches arise adjacent to each other from the posterolateral segment of the common trunk
- Type III: The right and left branches originate separately from the right and left lateral segments of the common trunk.
- Type IV: Neither of the branches arise from the common trunk, but are perfused by aortopulmonary collaterals. This type is now categorized as a form of pulmonary atresia with a ventricular septal defect rather than TA.
The Van Praagh classification system is based on where the branch pulmonary arteries arise from the trunk as well as the development of the aortic arch and the presence of a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). Each type may include a modifier “A” (with VSD) of “B” (intact ventricular septum).
- Type 1: The main pulmonary is present and bifurcates into the left and right pulmonary arteries (same as Collette and Edwards classification).
- Type 2: The right and left branch pulmonary arteries arise from the common trunk.
- Type 3: One branch pulmonary artery (typically the right) arises from the common trunk and the other arises from a PDA or the aorta.
- Type 4: This type is defined by presence of aortic arch hypoplasia, coarctation or interrupted aortic arch and a large PDA.
Common Associated anomalies:
- Ventricular Septal Defect- A VSD is present in the vast majority of cases. It is usually large and conoventricular.
- Aortic arch anomalies- Approximately 30% of patients with TA have a right aortic arch and 12% have aortic arch hypoplasia or an interrupted aortic arch.
- Truncal valve anomalies- The leaflets are usually thickened. The valve is most commonly tricuspid, but may also be bicuspid, quadricuspid or pentacuspid (rare) valve.
- Coronary artery anomalies- atypical origin, single coronary, or narrowed ostia resulting in coronary stenosis