- The tricuspid and mitral valve leaflets appear thin with normal excursion
- The tricuspid valve appears normally positioned (slightly more inferiorly positioned/apically displaced compared to the mitral valve).
- Normal sized right and left atrium
- Normal sized right and left ventricle
- Normal right and left ventricular systolic function
- No pericardial effusion
- Normal laminar flow across the tricuspid valve
- Trivial tricuspid regurgitation (tiny blue jet at site of valve coaptation)
- Normal laminar flow across the mitral valve
- Trivial mitral regurgitation (narrow blue jet at site of valve coaptation)
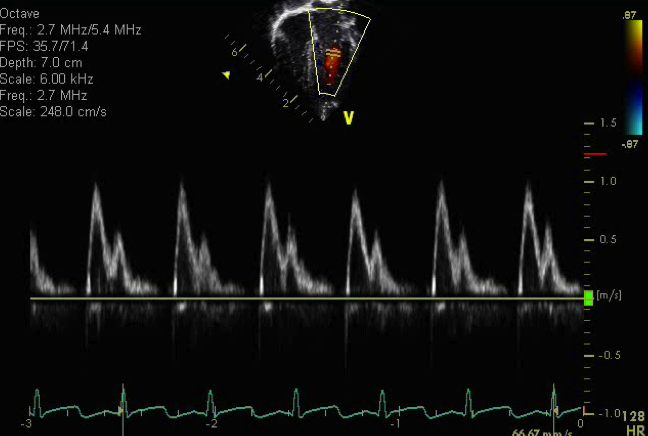
- Normal appearing pulse wave spectral Doppler of mitral valve inflow
- Normal appearing E wave (tallest peak which represents early mitral valve inflow into the left ventricle during diastole)
- Normal appearing A wave (smaller peak which represents atrial contraction at the end of diastole)
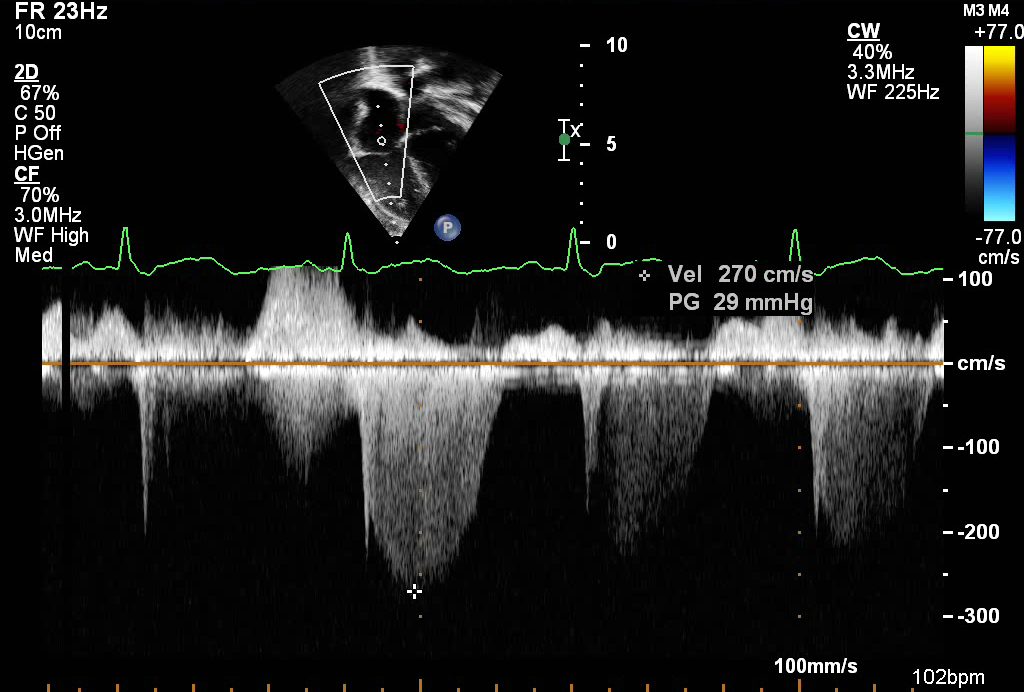
This clip demonstrates continuous wave Doppler across the tricuspid valve. The peak velocity obtained from the tricuspid regurgitation spectral Doppler jet is 2.7 meters/sec. Using the Bernoulli equation below we can estimate the right ventricular systolic pressure:
Pressure = 4V2
V= peak velocity of TR jet
i.e.= P= 4 (2.7)2 = 29 mmHg
Estimated RV systolic pressure = 29 mmHg + right atrial pressure (assumed to be 5 mmHg) in a healthy patient
Estimated RV systolic pressure = 29 mmHg + 5 mmHg = 34 mmHg
The apical four chamber view is a good view to assess atrial and ventricular size and function. It also can assess for tricuspid and mitral valve morphology and for evidence of stenosis or regurgitation.
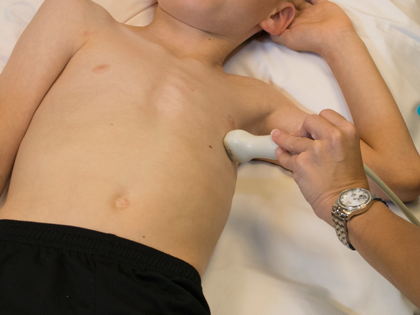
- Transducer placed on apical PMI (4th or 5th intercostal space)
- Midclavicular line at the apical PMI (point of maximal intensity)
- Notch at 3 o'clock
- Ventricular septal defects
- Atrial septal defects (not optimal view, but can appreciate larger defects)
- Tricuspid valve abnormalities
- Tricuspid valve prolapse
- Tricuspid stenosis or regurgitation
- Ebstein's anomaly
- Mitral valve abnormalties
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Mitral arcade
- Supravalvar mitral ring
- Parachute mitral valve
- Mitral regurgitation
- Mitral stenosis
- Pulmonary venous abnormalities
- Total anomalous pulmonary venous return or connection (confluence)
- Cor triatriatum
- Pulmonary vein stenosis
- Right atrial dilation
- Left atrial dilation
- Right ventricular dilation or hypertrophy
- Right ventricular dysfunction
- Left ventricular dilation or hypertrophy
- Left ventricular dysfunction
- Pericardial effusion