- The distal right ventricular ouflow tract appears of appropriate caliber.
- The pulmonary valve leaflets appear thin and mobile with good diastolic excursion.
- The main pulmonary artery appears of normal size.
- Color Doppler flow across the distal right ventricular outflow tract and main pulmonary artery.
- Normal laminar flow across the pulmonary valve
- Trivial pulmonary regurgitation (denoted by the narrow red jet at the point of valve coaptation).
Estimating pulmonary artery pressures from pulmonary regurgitation
- End diastolic PA pressure = Pulmonary regurgitation end diastolic peak gradient + right atrial pressure
- Mean PA pressure = Peak diastolic pulmonary regurgitation gradient + right atrial pressure
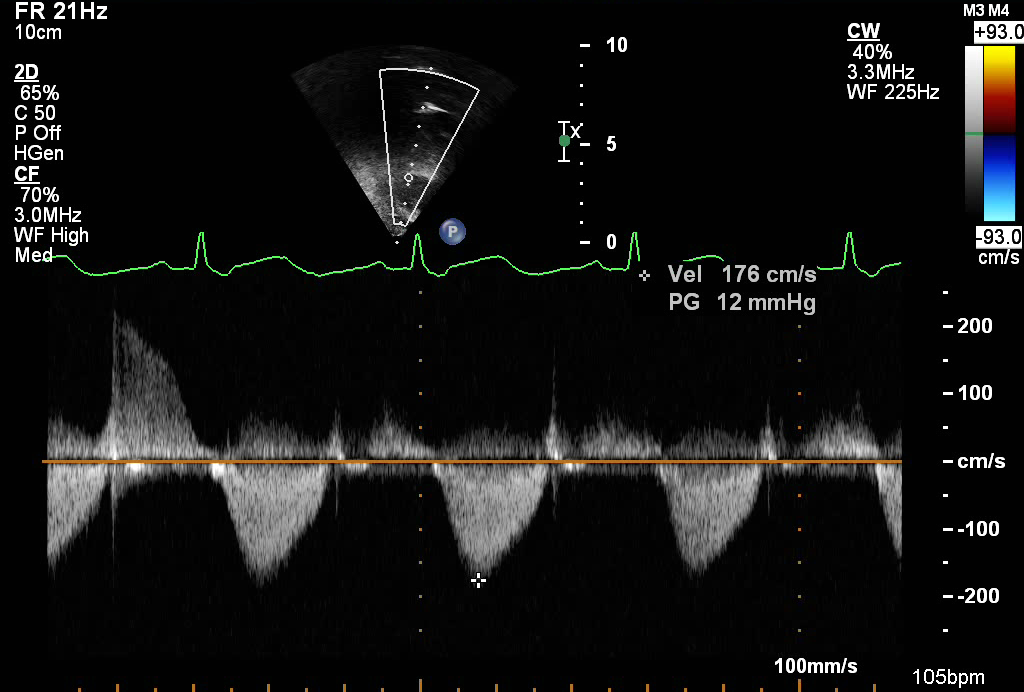
This continuous wave spectral Doppler clip across the RVOT and pulmonary valve. The Doppler envelope at the far left of the screen (above the baseline) demonstrates pulmonary regurgitation. The peak diastolic velocity (denoted by the symbol PV) and end diastolic velocity (denoted by the symbol E) can be measured and used to estimate the end diastolic PA pressure and Mean PA pressure (see example below).
- Pulmonary valve peak velocity (PV) = 2.0 meters/sec
- Pulmonary valve end diastolic velocity (E) = 1.5 meters/sec
Using Bernoulli equation (P = 4V2) the peak gradient can be obtained:
End diastolic PA pressure = 4(1.5)2 = 9 mmHg + right atrial pressure
Mean PA pressure = 4 (2.0)2 = 16 mmHg + right atrial pressure
The parasternal long axis view tilted anteriorly is an excellent view to profile the distal right ventricular outflow tract, assess the pulmonary valve morphology and main pulmonary artery.
.png)
- Transducer placed at the left sternal border
- 3rd or 4th intercostal space
- Notch pointed towards patient's right shoulder
- Angle transducer anteriorly towards patient's left shoulder (tilt tail of transducer down)
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
- Pulmonary valve abnormality
- Pulmonary valve stenosis
- Supravalvar pulmonary stenosis
- Pulmonary regurgitation
- RVOT obstruction
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Double chambered right ventricle
- Right ventricular outflow tract aneurysm