- Color Tissue Doppler Imaging
- Tissue Doppler color Doppler display of the heart from an apical 4 chamber view
- For pulse wave tissue Doppler interrogation
- Align the cursor along the lateral portion of the mitral valve annulus, medial portion of the mitral annulus and lateral portion of the tricuspid valve annulus
- Try to align the cursor as parallel to the myocardium as possible
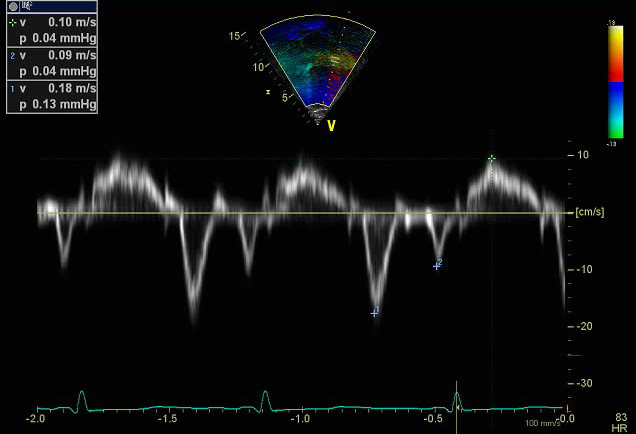
- Pulse wave tissue Doppler imaging of the lateral mitral valve annulus
- The sample volume should be positioned at or 1 cm within the lateral insertion site of the mitral leaflets to cover the longitudinal excursion of the annulus in systole and diastole
- Minimal angulation (<20 degrees) between the ultrasound beam and plane of cardiac motion as this is an angle dependent measure
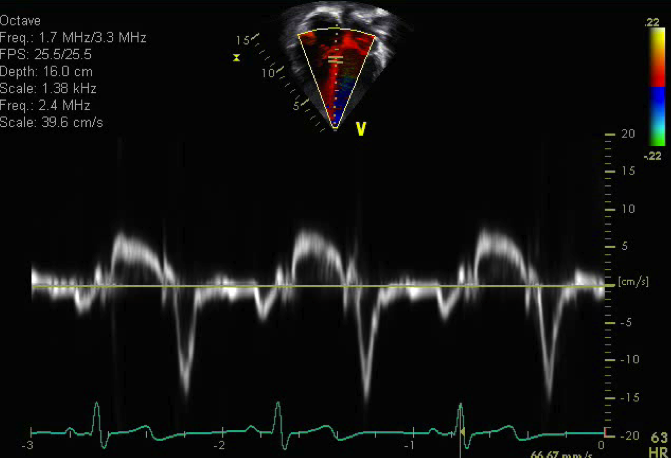
- Pulse wave tissue Doppler imaging of the medial mitral valve annulus
- The sample volume should be positioned at or 1 cm within the septal insertion site of the mitral leaflets to cover the longitudinal excursion of the annulus in both systole and diastole
- Minimal angulation (<20 degrees) between the ultrasound beam and plane of cardiac motion as this is an angle dependent measure
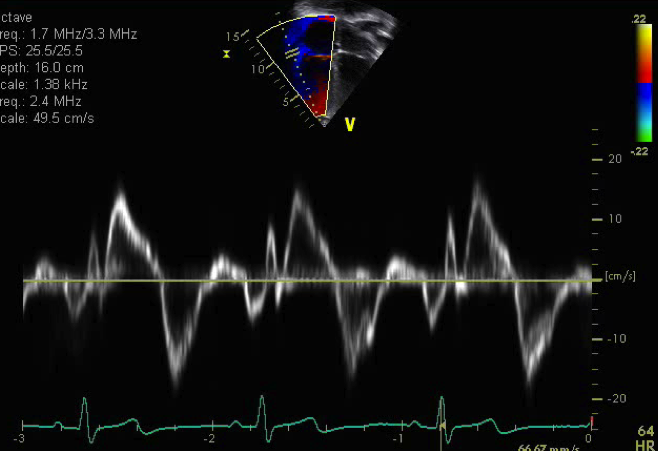
- Pulse wave Tissue Doppler imaging of the lateral tricuspid valve annulus
- The sample volume should be positioned at or 1 cm within the lateral insertion site of the tricuspid leaflets to cover longitudinal excursion in both systole and diastole
- Minimal angulation (<20 degrees) between the ultrasound beam and plane of cardiac motion as this is an angle dependent measure
Tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) can be obtained using pulse-wave Doppler or color Doppler. Pulse wave Doppler TDI is used to measure the peak velocity of the ventricular myocardium. It is an angle dependent measurement so it is important to allign your ultrasound as parallel to the myocardium as possible. This lends itself well to the apical four chamber view to assess the these fibers as they are longitudinally oriented fibers. This can be a good surrogate to assess left ventricular relaxation and TDI velocities are obtain impaired and blunted in the setting of diastolic dysfunction.
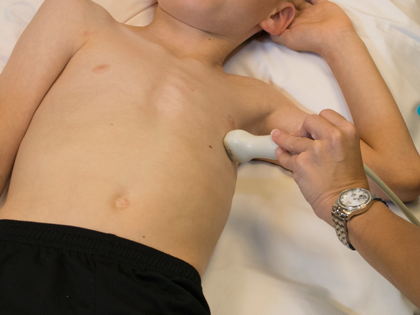
- Transducer placed on apical PMI (4th or 5th intercostal space)
- Midclavicular line at the apical point of maximal intensity (PMI)
- Notch at 3 o'clock
- Diastolic dysfunction
- Isolated diastolic dysfunction
- Transplant vasculopathy or rejection
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy